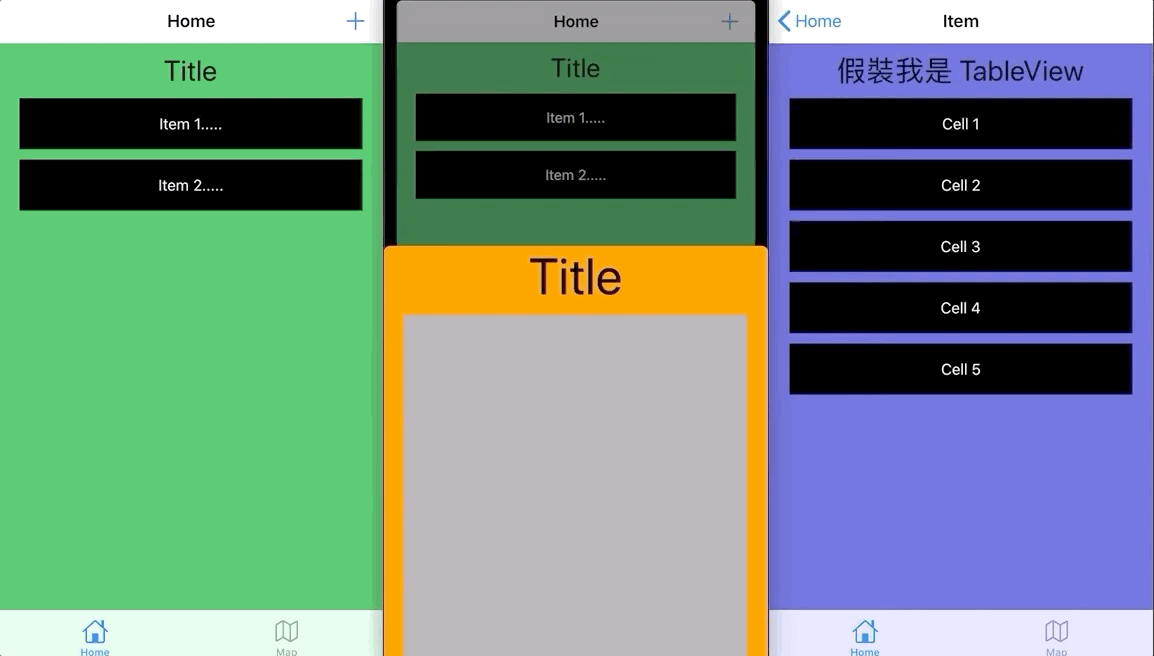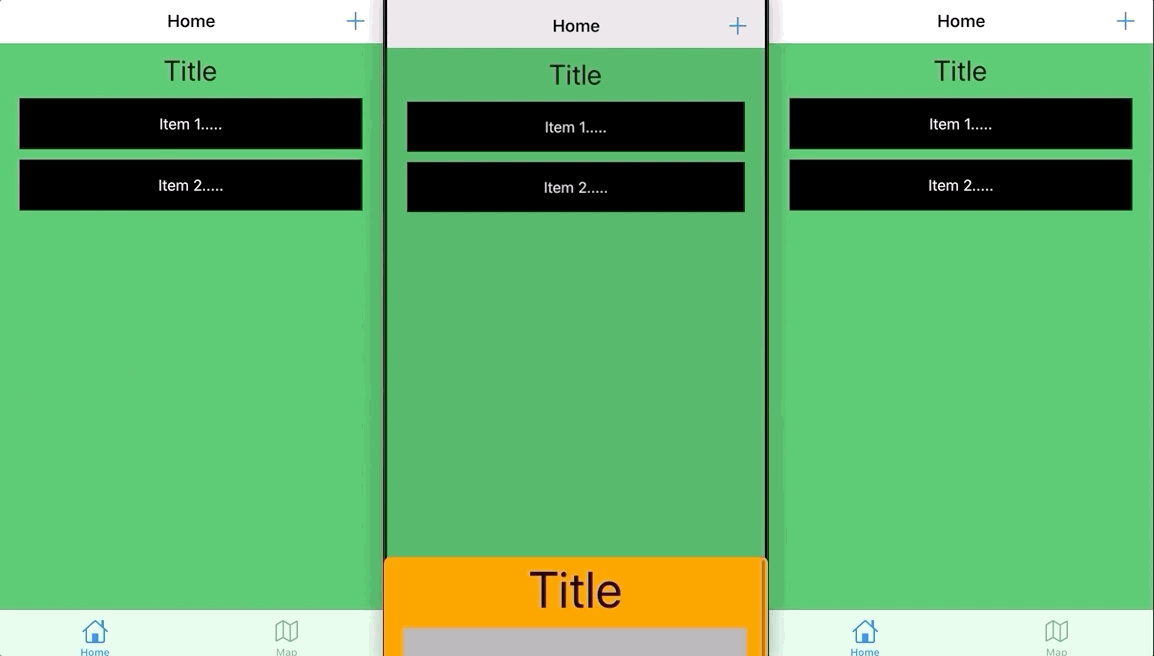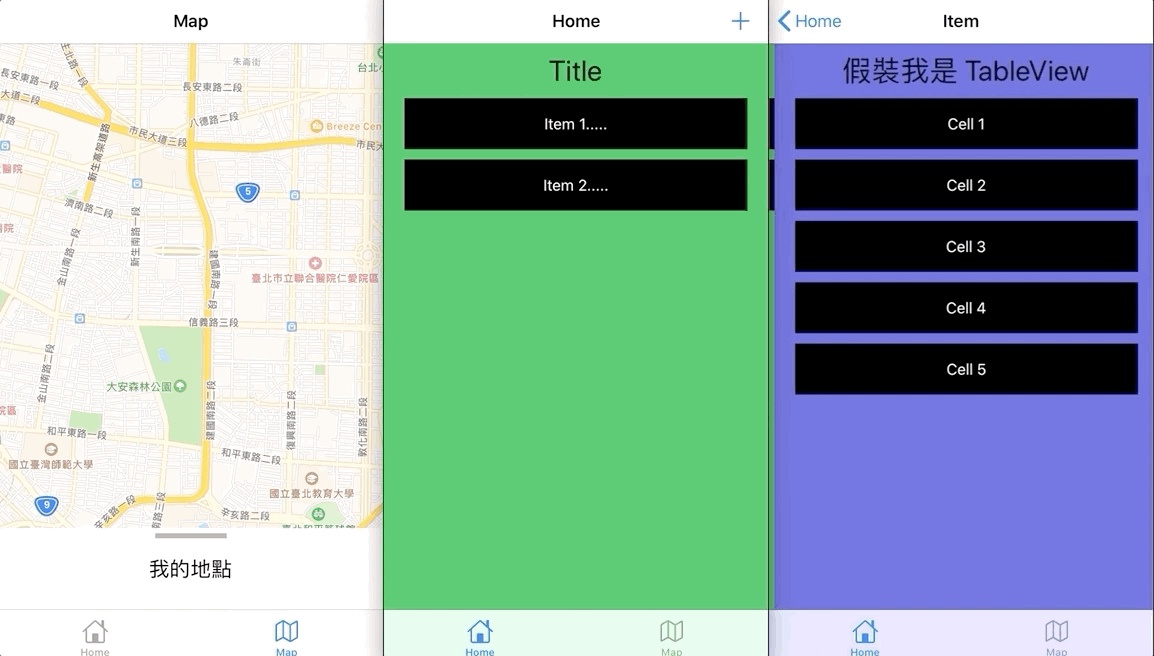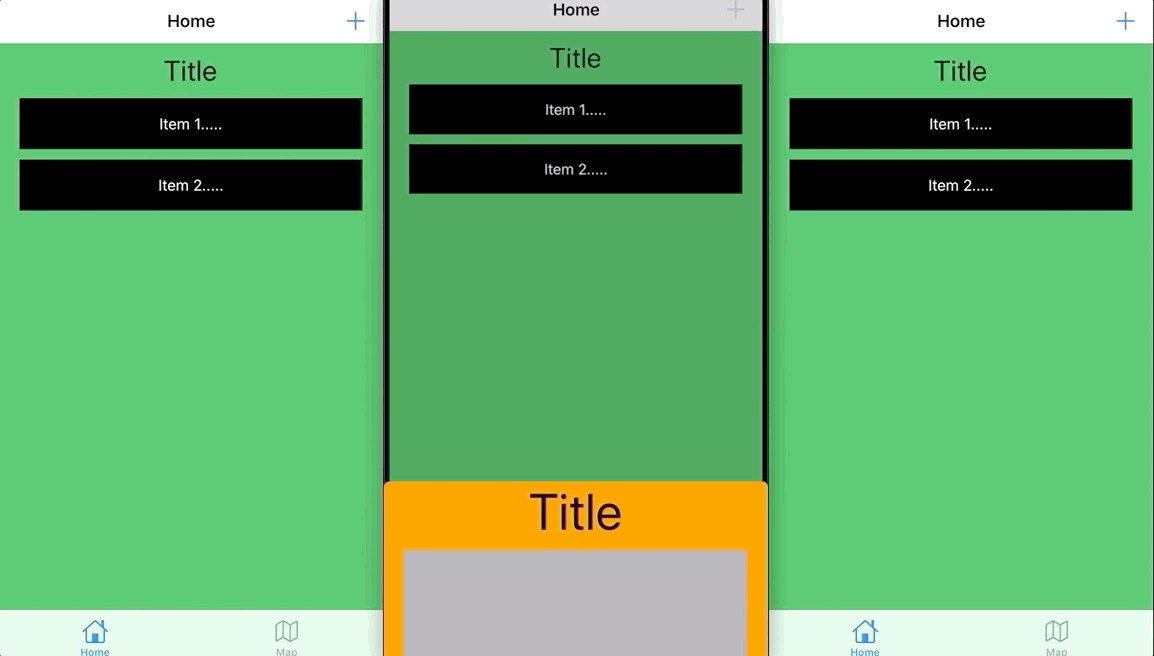
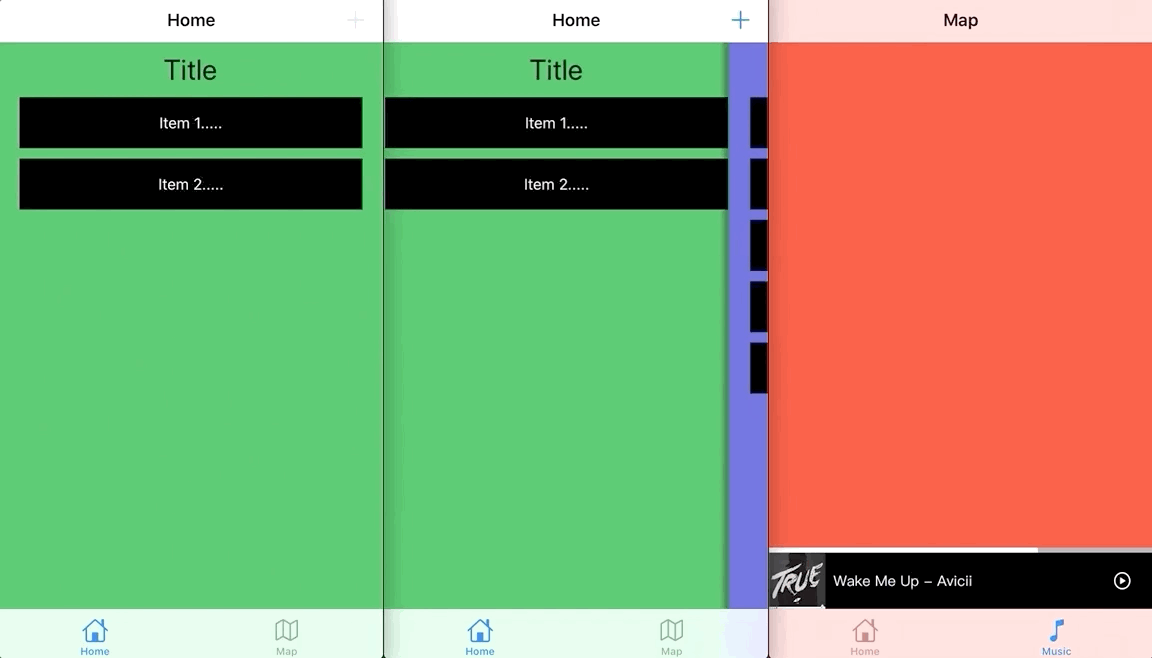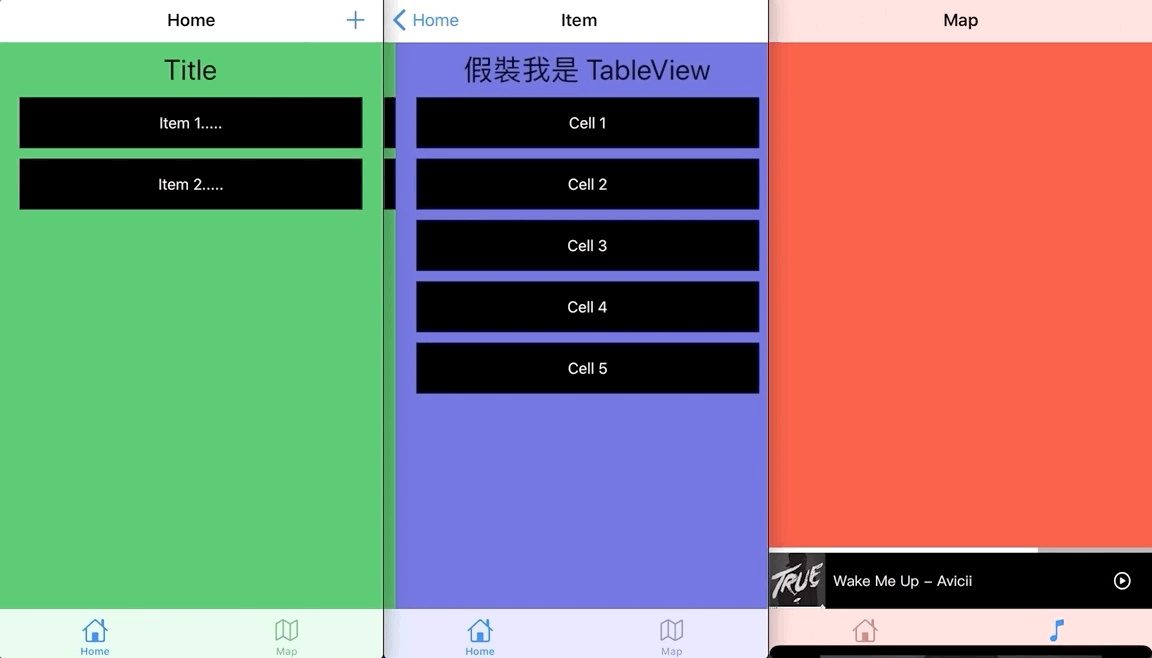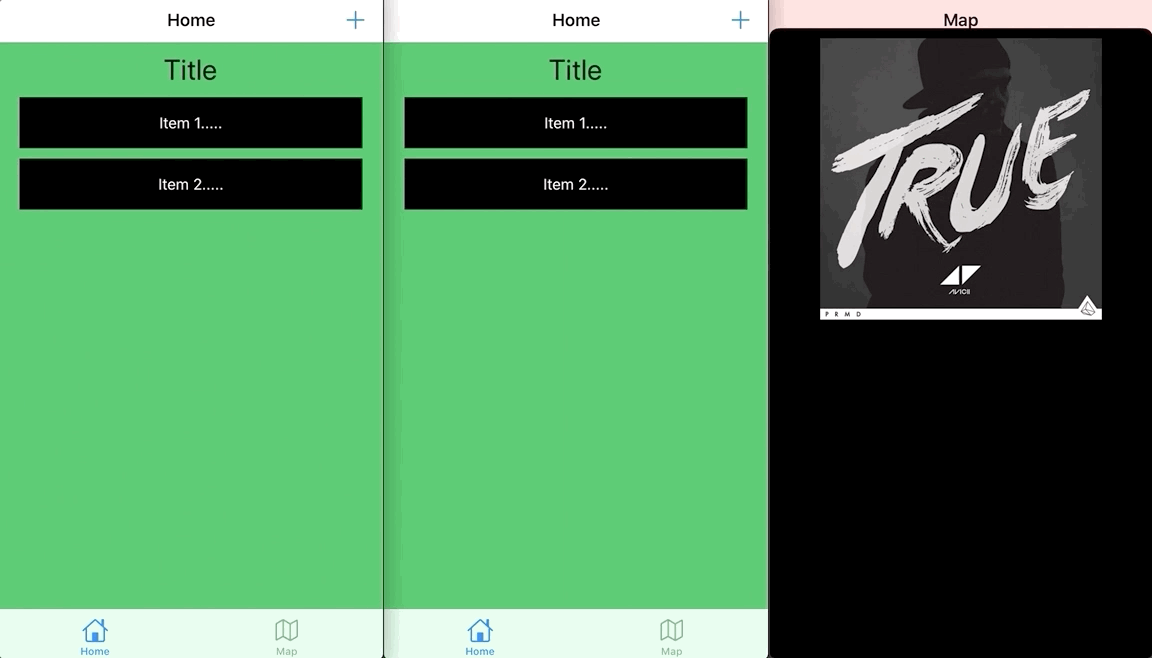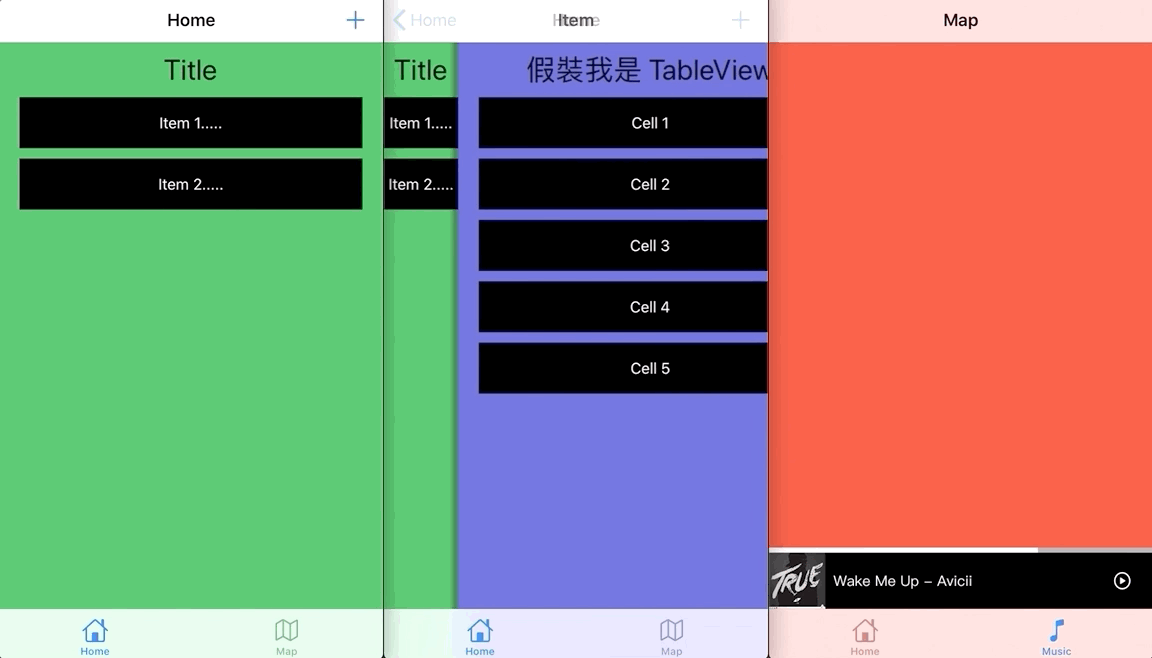
iOS UIViewController 轉場|下拉關閉・上拉出現・全頁右滑返回 完全解説
iOS開発者向けにUIViewControllerの下拉閉じる・上拉表示・全頁右滑戻るの実装方法を具体的に解説。ユーザー体験を向上させるスムーズな画面遷移を実現し、操作性を劇的に改善します。
本記事は AI による翻訳をもとに作成されています。表現が不自然な箇所がありましたら、ぜひコメントでお知らせください。
記事一覧
iOS UIViewController のトランジションに関するあれこれ
UIViewController の下方向スワイプで閉じる/上方向スワイプで表示/全画面右スワイプで戻る 効果の完全解説
はじめに
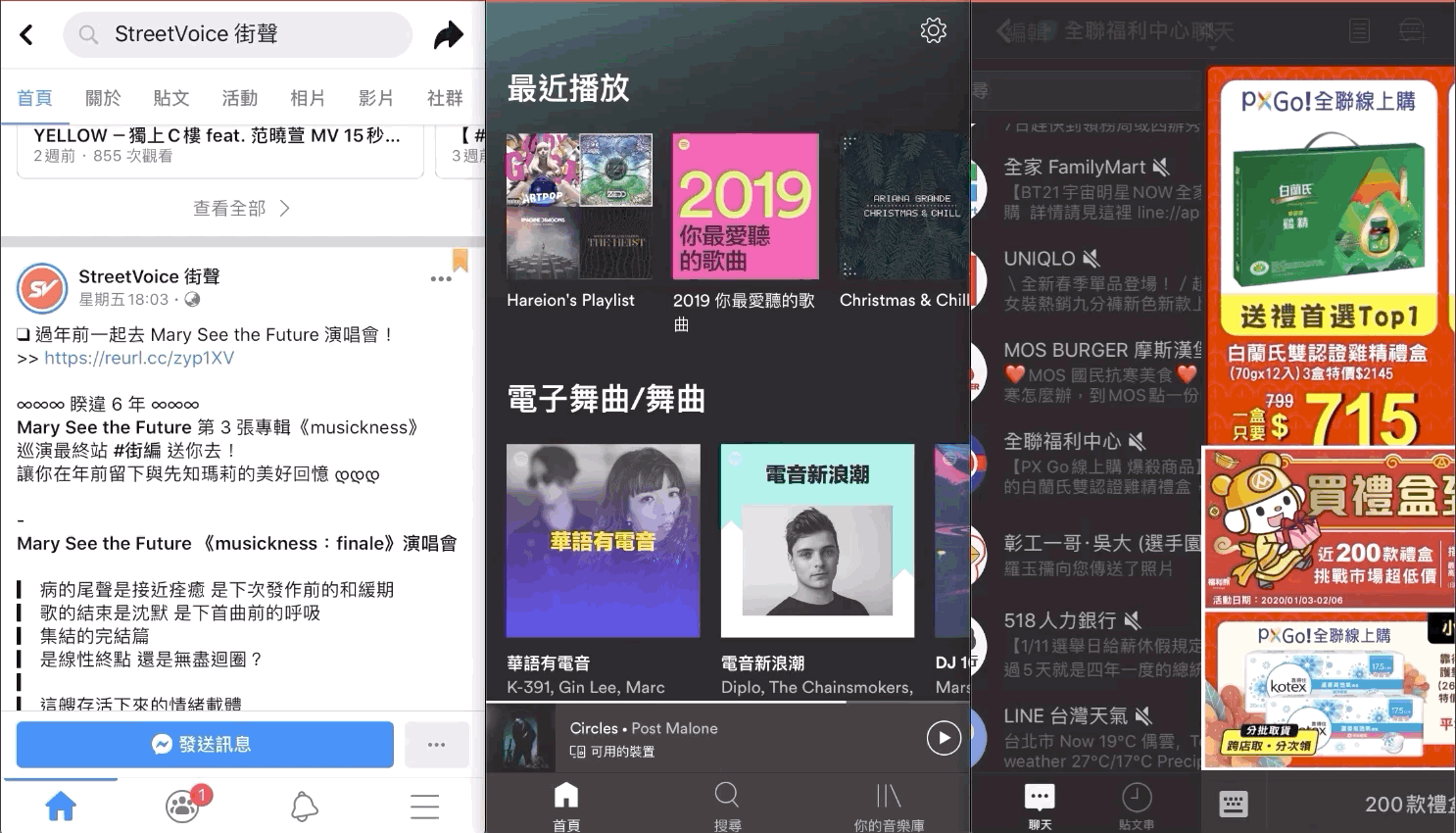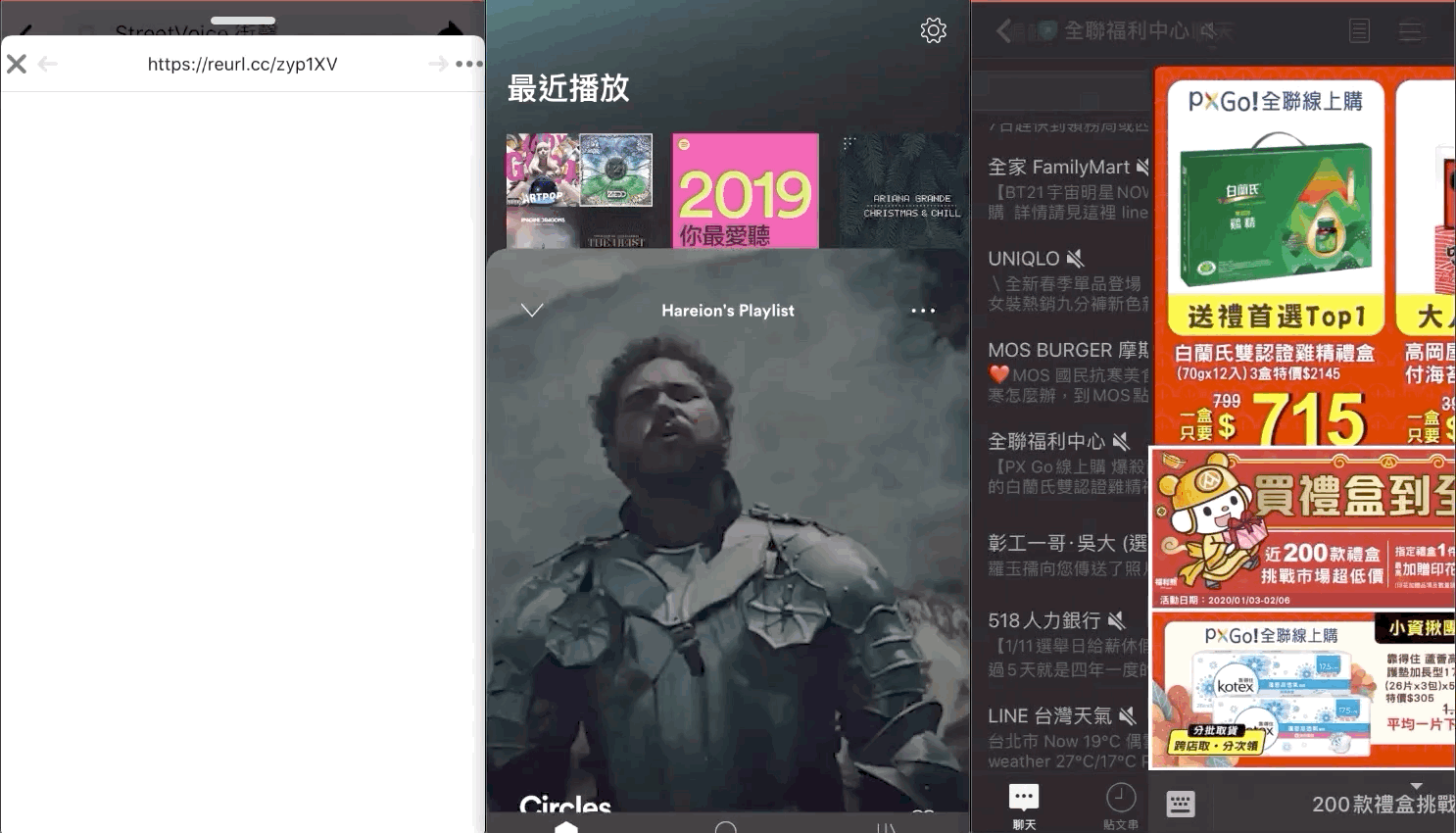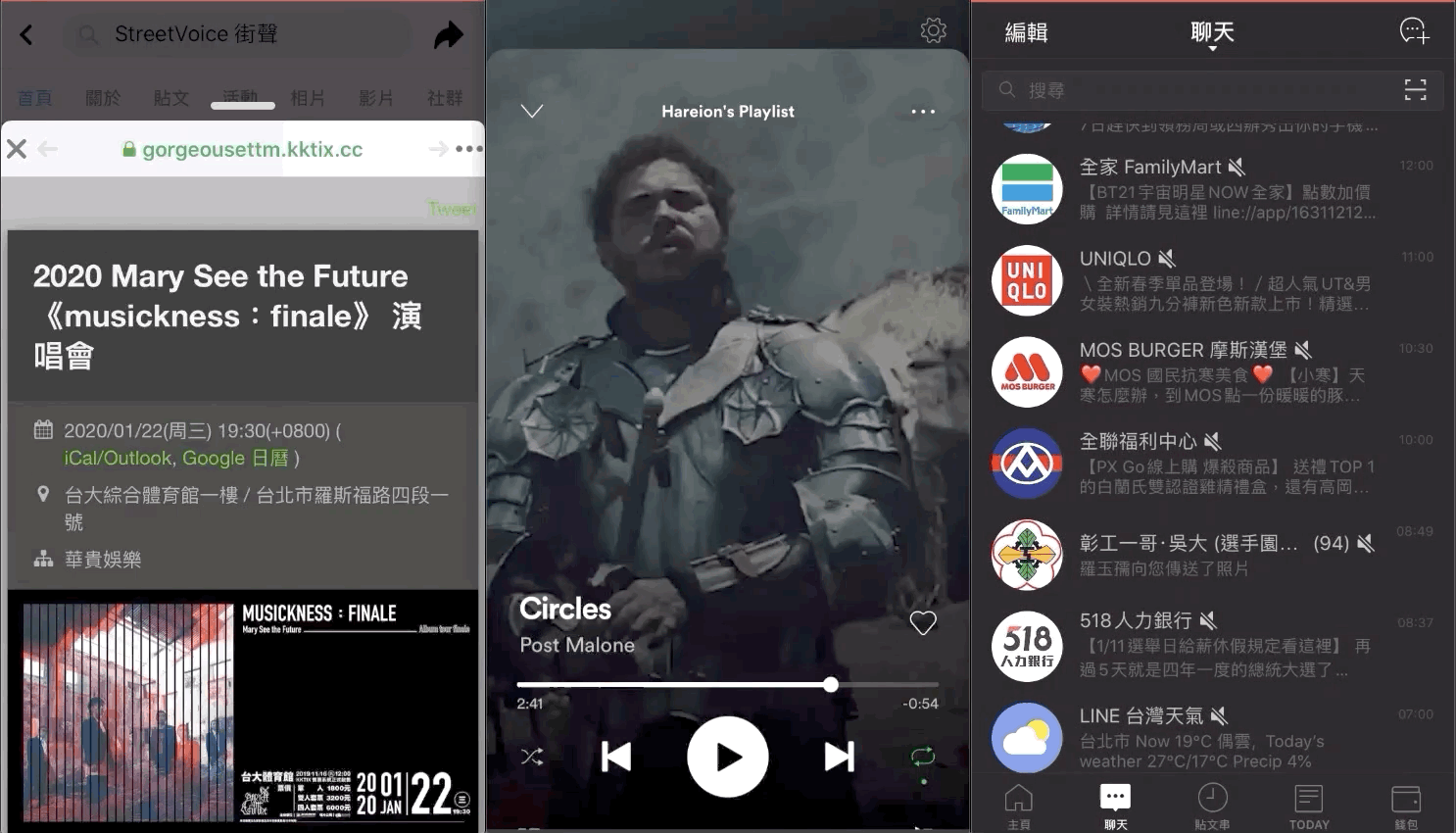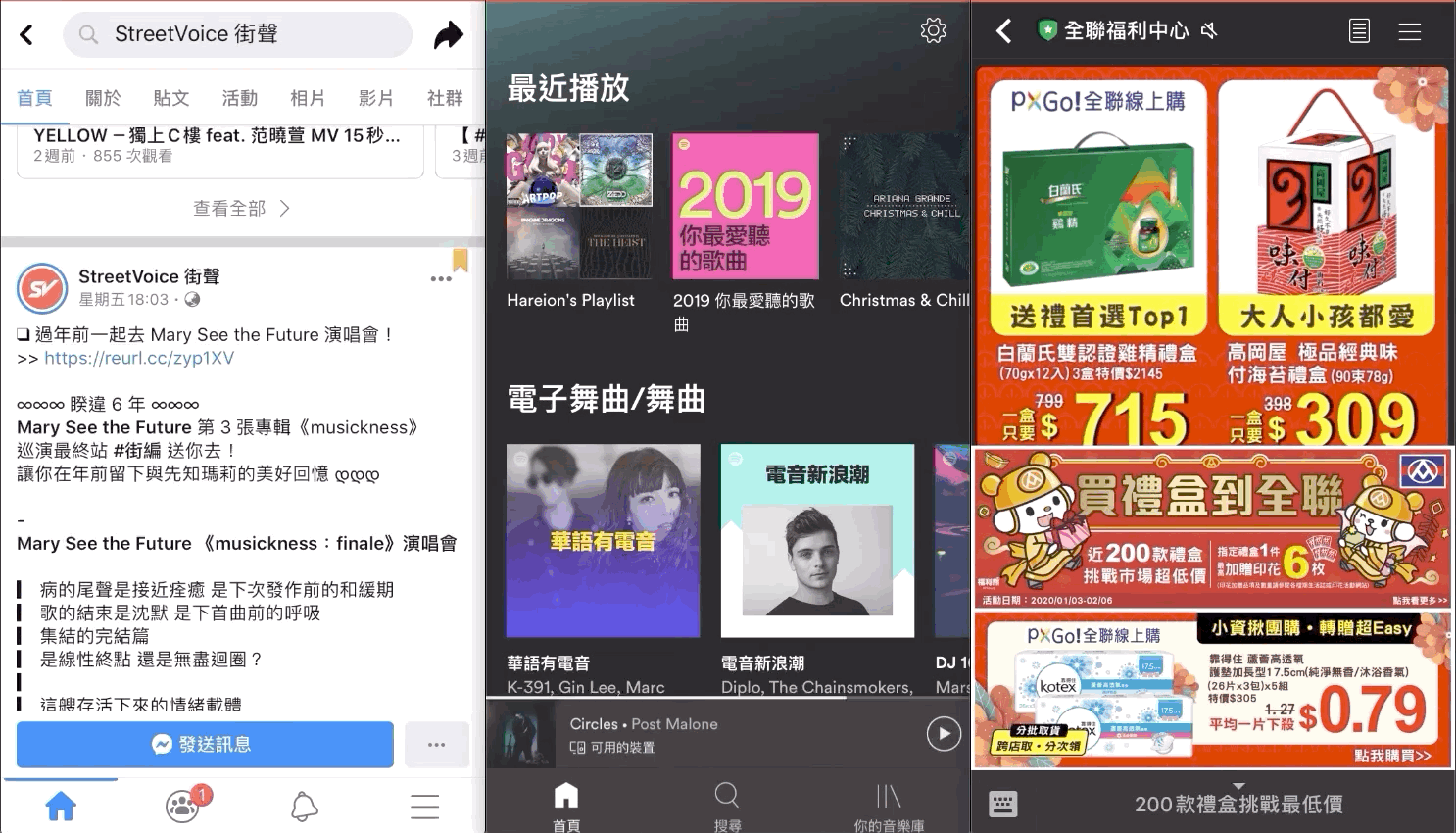
ずっと気になっていたのは、Facebook、Line、Spotifyなどのよく使われるアプリが「Presentされた UIViewController を下にスワイプして閉じる」「上にスワイプして UIViewController がフェードインする」「全画面で右スワイプによる戻るジェスチャーをサポートする」といった効果をどう実装しているのかということです。
これらの効果は標準で搭載されておらず、下にスワイプして閉じる動作も iOS 13 以降でようやくシステムのカードスタイルとしてサポートされました。
探索の道
キーワードの付け方が悪いのか、そもそも情報が少ないのか、このような機能の実装方法がなかなか見つかりません。見つかる情報も曖昧で断片的で、寄せ集めるしかありません。
最初、自分で調べていたときに UIPresentationController という API を見つけ、他の資料は深く調べずに、この方法を UIPanGestureRecognizer と組み合わせて、かなり原始的な方法で下にスワイプして閉じる効果を実装しました。しかし、どこかおかしいと感じていて、もっと良い方法があるはずだと思っていました。
最近新しいプロジェクトに関わるまで、大先輩の記事 を拝読し、視野が広がり、より美しく柔軟なAPIの使い方があることに気づきました。
本記事は一方で自己記録として、もう一方で同じ悩みを持つ方の助けになればと思っています。
内容が少し多いため、面倒な方は直接最後までスクロールしてサンプルを見るか、GitHubのプロジェクトをダウンロードしてご確認ください!
iOS 13 カードスタイルの表示ページ
まず最新のシステム内蔵の効果について説明します
iOS ≥ 13 以降の UIViewController.present(_:animated:completion:)
デフォルトの modalPresentationStyle の効果は UIModalPresentationAutomatic のカードスタイル表示です。以前の全画面表示を維持したい場合は、明示的に UIModalPresentationFullScreen を指定する必要があります。
内蔵カレンダーの追加エフェクト
下にスワイプして閉じる動作を無効にする方法と閉じる前の確認方法?
より良いユーザー体験のためには、下にスワイプして閉じる操作を開始した際に入力データがあるかどうかを確認し、ある場合はユーザーに破棄して離脱するかどうかを確認する必要があります。
この部分はAppleが既に考慮してくれているので、UIAdaptivePresentationControllerDelegate のメソッドを実装するだけで済みます。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
import UIKit
class DetailViewController: UIViewController {
private var onEdit:Bool = true;
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// デリゲートを設定
self.presentationController?.delegate = self
// UIViewControllerがnavigationControllerに埋め込まれている場合:
//self.navigationController?.presentationController?.delegate = self
// 下にスワイプして閉じる動作を無効化(1):
self.isModalInPresentation = true;
}
}
// デリゲート実装
extension DetailViewController: UIAdaptivePresentationControllerDelegate {
// 下にスワイプして閉じる動作を無効化(2):
func presentationControllerShouldDismiss(_ presentationController: UIPresentationController) -> Bool {
return false;
}
// 下にスワイプして閉じる動作がキャンセルされた時、スワイプジェスチャーがトリガーされる
func presentationControllerDidAttemptToDismiss(_ presentationController: UIPresentationController) {
if (onEdit) {
let alert = UIAlertController(title: "データが保存されていません", message: nil, preferredStyle: .actionSheet)
alert.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "破棄して離れる", style: .default) { _ in
self.dismiss(animated: true)
})
alert.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "編集を続ける", style: .cancel, handler: nil))
self.present(alert, animated: true)
} else {
self.dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil)
}
}
}
下にスワイプして閉じる動作を無効にするには、UIViewController の変数 isModalInPresentation を false に設定するか、UIAdaptivePresentationControllerDelegate の presentationControllerShouldDismiss を実装して true を返す方法のいずれかを選択します。
UIAdaptivePresentationControllerDelegate presentationControllerDidAttemptToDismiss このメソッドは 下にスワイプして閉じる操作がキャンセルされた時 のみ呼び出されます。
ちなみに…
カードスタイルの表示ページはシステム上「Sheet」と呼ばれ、動作は「FullScreen」とは異なります。
今日
RootViewControllerはHomeViewControllerであると仮定する
カードスタイル表示時(UIModalPresentationAutomatic)では:
HomeViewControllerがDetailViewControllerをPresentする時…
HomeViewControllerのviewWillDisappear/viewDidDisappearは一切呼ばれません。
DetailViewControllerがDismissされるとき…
HomeViewControllerのviewWillAppear/viewDidAppearは呼び出されません。
⚠️ XCODE 11以降のバージョンでビルドした iOS 13以上のアプリは、デフォルトでカードスタイルのプレゼンテーション(UIModalPresentationAutomatic)を使用します
もし以前に viewWillAppear/viewWillDisappear/viewDidAppear/viewDidDisappear にロジックを入れていた場合は、特に注意してよく確認してください! ⚠️
システム内蔵のものを見た後は、本記事の本題に入りましょう!これらの効果をどうやって自作するか?
どこでトランジションアニメーションを行うことができる?
まず、どこでウィンドウ切り替えのトランジションアニメーションができるか整理します。
UITabBarController/UIViewController/UINavigationController
UITabBarController の切り替え時
UITabBarController に delegate を設定し、animationControllerForTransitionFrom メソッドを実装することで、UITabBarController の切り替え時にカスタムトランジションアニメーションを適用できます。
システムのデフォルトはアニメーションなしで、上の画像はフェードイン・フェードアウトの切り替え効果です。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
import UIKit
class MainTabBarViewController: UITabBarController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
self.delegate = self
}
}
extension MainTabBarViewController: UITabBarControllerDelegate {
func tabBarController(_ tabBarController: UITabBarController, animationControllerForTransitionFrom fromVC: UIViewController, to toVC: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
// UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning を返す
}
}
UIViewController Present/Dismiss 時
もちろん、Present/Dismiss の UIViewController では適用するアニメーション効果を指定できます。そうでなければこの記事は存在しませんねXD;ただし、単純に Present アニメーションだけで手勢制御をしない場合は、UIPresentationController を直接使うと便利で簡単です(詳細は記事末の参考資料をご覧ください)。
システムのデフォルトは上にスワイプで表示、下にスワイプで非表示です。カスタマイズする場合はフェードイン、角丸、表示位置の制御などの効果を追加できます。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
import UIKit
class HomeAddViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
self.modalPresentationStyle = .custom
self.transitioningDelegate = self
}
}
extension HomeAddViewController: UIViewControllerTransitioningDelegate {
func animationController(forPresented presented: UIViewController, presenting: UIViewController, source: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
// nilを返すとデフォルトのアニメーションが実行される
return // UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning プレゼント時に適用するアニメーション
}
func animationController(forDismissed dismissed: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
// nilを返すとデフォルトのアニメーションが実行される
return // UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning ディスミス時に適用するアニメーション
}
}
任意の
UIViewControllerはtransitioningDelegateを実装してPresent/Dismissアニメーションを通知できる;UITabBarController、UINavigationController、UITableViewControllerなども可能
UINavigationController の Push/Pop 時
UINavigationController はアニメーションを変更する必要がほとんどないです。なぜなら、システム標準の左スワイプで表示、右スワイプで戻るアニメーションが最適だからです。この部分をカスタマイズする場合は、シームレスな UIViewController の左右切り替え効果を実現するためかもしれません。
全画面でのジェスチャー戻るを実現するために、カスタムPOPアニメーションと連携し、自分で戻るアニメーションを実装する必要があります。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
import UIKit
class HomeNavigationController: UINavigationController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
self.delegate = self
}
}
extension HomeNavigationController: UINavigationControllerDelegate {
func navigationController(_ navigationController: UINavigationController, animationControllerFor operation: UINavigationController.Operation, from fromVC: UIViewController, to toVC: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
if operation == .pop {
return // UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning 戻る時に適用するアニメーション
} else if operation == .push {
return // UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning プッシュ時に適用するアニメーション
}
// nil を返すとデフォルトのアニメーションが使われる
return nil
}
}
インタラクティブと非インタラクティブなアニメーション?
アニメーション実装やジェスチャー制御の前に、まずインタラクティブとノンインタラクティブについて説明します。
インタラクティブアニメーション: UIPanGestureRecognizer などのジェスチャーでトリガーされるアニメーション
非インタラクティブアニメーション: システムが呼び出すアニメーション、例えば self.present()
アニメーション効果はどうやって実装する?
どこで実装できるか説明したので、次はアニメーション効果の作り方を見ていきましょう。
私たちは UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning という Protocol を実装し、その中でウィンドウに対してアニメーションを行う必要があります。
一般的な遷移アニメーション: UIView.animate
直接 UIView.animate を使ってアニメーション処理を行う場合、UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning では transitionDuration でアニメーションの長さを指定し、animateTransition でアニメーション内容を実装する必要があります。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
import UIKit
class SlideFromLeftToRightTransition: NSObject, UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning {
func transitionDuration(using transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning?) -> TimeInterval {
return 0.4
}
func animateTransition(using transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning) {
// 使用可能なパラメータ:
// 表示する対象の UIViewController の View 内容を取得:
let toView = transitionContext.view(forKey: .to)
// 表示する対象の UIViewController を取得:
let toViewController = transitionContext.viewController(forKey: .to)
// 表示する対象の UIViewController の View の初期 Frame 情報を取得:
let toInitalFrame = transitionContext.initialFrame(for: toViewController!)
// 表示する対象の UIViewController の View の最終 Frame 情報を取得:
let toFinalFrame = transitionContext.finalFrame(for: toViewController!)
// 現在の UIViewController の View 内容を取得:
let fromView = transitionContext.view(forKey: .from)
// 現在の UIViewController を取得:
let fromViewController = transitionContext.viewController(forKey: .from)
// 現在の UIViewController の View の初期 Frame 情報を取得:
let fromInitalFrame = transitionContext.initialFrame(for: fromViewController!)
// 現在の UIViewController の View の最終 Frame 情報を取得:(閉じるアニメーション時に以前の表示アニメーションの最終Frameを取得可能)
let fromFinalFrame = transitionContext.finalFrame(for: fromViewController!)
//toView.frame.origin.y = UIScreen.main.bounds.size.height
UIView.animate(withDuration: transitionDuration(using: transitionContext), delay: 0, options: [.curveLinear], animations: {
//toView.frame.origin.y = 0
}) { (_) in
if (!transitionContext.transitionWasCancelled) {
// アニメーションが中断されていない
}
// システムにアニメーション完了を通知
transitionContext.completeTransition(!transitionContext.transitionWasCancelled)
}
}
}
To と From:
もし今日
HomeViewControllerがDetailViewControllerをPresent/Pushする場合、
From = HomeViewController / To = DetailViewController
DetailViewControllerがDismiss/Popされるとき、
From = DetailViewController / To = HomeViewController
⚠️⚠️⚠️⚠️⚠️
公式には
transitionContext.viewControllerの .view ではなく、transitionContext.viewからビューを取得することが推奨されています。
しかしここで問題があります。Present/Dismiss アニメーションを行う際に
modalPresentationStyle = .customの場合;
Present 時に
transitionContext.view(forKey: .from)は nil になります、
Dismiss 時に
transitionContext.view(forKey: .to)を使っても nil になります;
やはり viewController.view から値を取得して使用する必要がある。
⚠️⚠️⚠️⚠️⚠️
transitionContext.completeTransition(!transitionContext.transitionWasCancelled)アニメーション完了時に必ず呼び出す必要があります。そうしないと画面がフリーズします;
しかし
UIView.animateは実行するアニメーションがない場合、completionが呼ばれないため、前述のメソッドが呼ばれません。したがって、アニメーションが必ず実行されるようにしてください(例:yを100から0に変える)。
ℹ️ℹ️ℹ️ℹ️ℹ️
アニメーションに関わる
ToView/FromViewが複雑であったりアニメーション時に問題がある場合、snapshotView(afterScreenUpdates:)を使ってスクリーンショットを取得し、それをアニメーション表示に使う方法があります。まずスクリーンショットを取得し、transitionContext.containerView.addSubview(snapShotView)でレイヤーに追加します。その後、元のToView/FromViewを非表示にし(isHidden = true)、アニメーション終了時にsnapShotView.removeFromSuperview()を呼び出して削除し、元のToView/FromViewを再表示します(isHidden = false)。
中断可能で再開可能なトランジションアニメーション: UIViewPropertyAnimator
また、iOS ≥ 10 の新しいアニメーションクラスを使ってアニメーションを実装することもできます。
個人の好みやアニメーションの細かさによって選択してください。
公式の推奨はインタラクティブな場合は UIViewPropertyAnimator を使うことですが、インタラクティブ・非インタラクティブ(ジェスチャー制御)に関わらず、一般的には UIView.animate で十分です。
UIViewPropertyAnimator のトランジションアニメーションは中断・再開が可能ですが、実際にどこで使うかは分かりません。興味がある方は こちらの記事 を参照してください。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
import UIKit
class FadeInFadeOutTransition: NSObject, UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning {
private var animatorForCurrentTransition: UIViewImplicitlyAnimating?
func interruptibleAnimator(using transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning) -> UIViewImplicitlyAnimating {
// 現在の遷移アニメーションがある場合はそれを返す
if let animatorForCurrentTransition = animatorForCurrentTransition {
return animatorForCurrentTransition
}
// パラメータは前述と同じ
// fromView.frame.origin.y = 100
let animator = UIViewPropertyAnimator(duration: transitionDuration(using: transitionContext), curve: .linear)
animator.addAnimations {
// fromView.frame.origin.y = 0
}
animator.addCompletion { (position) in
transitionContext.completeTransition(!transitionContext.transitionWasCancelled)
}
// アニメーションを保持
self.animatorForCurrentTransition = animator
return animator
}
func transitionDuration(using transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning?) -> TimeInterval {
return 0.4
}
func animateTransition(using transitionContext: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning) {
// 非インタラクティブの場合はこちらが呼ばれるので、インタラクティブのアニメーションを実行する
let animator = self.interruptibleAnimator(using: transitionContext)
animator.startAnimation()
}
func animationEnded(_ transitionCompleted: Bool) {
// アニメーション完了後にクリア
self.animatorForCurrentTransition = nil
}
}
インタラクティブな場合(後ほどコントローラについて詳しく説明します)は、
interruptibleAnimatorメソッドのアニメーションを使用します。インタラクティブでない場合は、animateTransitionメソッドを使用します。
継続や中断が可能な特性があるため、
interruptibleAnimatorは繰り返し呼び出される可能性があります。そのため、グローバル変数でアクセスして保持する必要があります。
Murmur…
実は最初、すべて新しい UIViewPropertyAnimator に切り替えて、みんなにも新しい方法を使うことを勧めたかったのですが、全画面ジェスチャーで戻る Pop アニメーションを作るときに奇妙な問題に遭遇しました。ジェスチャーを離してアニメーションが元に戻る際、上部のナビゲーションバーのアイテムが一瞬フェードイン・アウトしてチカチカするのです…原因が見つかりませんでしたが、UIView.animate に戻すとこの問題は起きませんでした。もし何か見落としがあれば教えてください<( _ _ )>。
問題の画像; + ボタンは前のページのものです
なので、安全のためにやはり従来の方法を使いましょう!
実際には異なるアニメーション効果ごとに個別のクラスを作成します。ファイルが多くなりすぎると感じたら、記事末尾のまとめた方法を参考にしてください。または、同じ連続した(Present + Dismiss)アニメーションを一緒にまとめても構いません。
transitionCoordinator
また、より細かい制御が必要な場合、例えば ViewController 内の特定のコンポーネントを転場アニメーションに合わせて変更したい場合は、UIViewController の transitionCoordinator を使って連携できます。私はこの部分は使っていませんが、興味があればこちらの記事を参照してください。
アニメーションをどう制御する?
ここが前述した「インタラクション」、つまり実際にはジェスチャーコントロールの部分です。本記事で最も重要な章であり、ジェスチャー操作とトランジションアニメーションの連動機能を実装することで、下にスワイプして閉じる機能や全画面スワイプで戻る機能を実現します。
デリゲートの設定:
前述の ViewController の代理アニメーション設計と同様に、インタラクション処理のクラスも代理を通じて ViewController に通知する必要があります。
UITabBarController: なし
UINavigationController (プッシュ/ポップ):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
import UIKit
class HomeNavigationController: UINavigationController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
self.delegate = self
}
}
extension HomeNavigationController: UINavigationControllerDelegate {
func navigationController(_ navigationController: UINavigationController, animationControllerFor operation: UINavigationController.Operation, from fromVC: UIViewController, to toVC: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
if operation == .pop {
return // UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning 戻る時に適用するアニメーション
} else if operation == .push {
return // UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning プッシュ時に適用するアニメーション
}
// nilを返すとデフォルトアニメーションが使われる
return nil
}
// インタラクティブな遷移の代理メソッドを追加:
func navigationController(_ navigationController: UINavigationController, interactionControllerFor animationController: UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning) -> UIViewControllerInteractiveTransitioning? {
// ここではPopかPushか判別できないため、アニメーション自体で判定する
if animationController is プッシュ時に適用するアニメーション {
return // UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition プッシュアニメーションのインタラクション制御
} else if animationController is 戻る時に適用するアニメーション {
return // UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition ポップアニメーションのインタラクション制御
}
// nilを返すとインタラクションなし
return nil
}
}
UIViewController(プレゼント/ディスミス):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
import UIKit
class HomeAddViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
self.modalPresentationStyle = .custom
self.transitioningDelegate = self
}
}
extension HomeAddViewController: UIViewControllerTransitioningDelegate {
func interactionControllerForDismissal(using animator: UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning) -> UIViewControllerInteractiveTransitioning? {
// nilを返すとインタラクション処理を行わない
return // UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition Dismiss時のインタラクション制御メソッド
}
func interactionControllerForPresentation(using animator: UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning) -> UIViewControllerInteractiveTransitioning? {
// nilを返すとインタラクション処理を行わない
return // UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition Present時のインタラクション制御メソッド
}
func animationController(forPresented presented: UIViewController, presenting: UIViewController, source: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
// nilを返すとデフォルトのアニメーションが使われる
return // UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning Present時に適用するアニメーション
}
func animationController(forDismissed dismissed: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
// nilを返すとデフォルトのアニメーションが使われる
return // UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning Dismiss時に適用するアニメーション
}
}
⚠️⚠️⚠️⚠️⚠️
interactionControllerFor などのメソッドを実装している場合、アニメーションが非インタラクティブ(例:self.present でシステムがトランジションを呼び出す場合)でも、これらのメソッドは呼ばれます;制御すべきは内部の
wantsInteractiveStartパラメータです(後述)。
アニメーションインタラクション処理クラス UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition:
次に、コアとなる実装である UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition について説明します。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
import UIKit
class PullToDismissInteractive: UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition {
// インタラクティブなジェスチャーを追加するUIView
private var interactiveView: UIView!
// 現在のUIViewController
private var presented: UIViewController!
// どれだけドラッグしたら完了とみなすかの閾値
private let thredhold: CGFloat = 0.4
// それぞれのトランジション効果に応じて情報をカスタマイズ可能
convenience init(_ presented: UIViewController, _ interactiveView: UIView) {
self.init()
self.interactiveView = interactiveView
self.presented = presented
setupPanGesture()
// デフォルト値、現在はインタラクティブなアニメーションではないことをシステムに通知
wantsInteractiveStart = false
}
private func setupPanGesture() {
let panGesture = UIPanGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: #selector(handlePan(_:)))
panGesture.maximumNumberOfTouches = 1
panGesture.delegate = self
interactiveView.addGestureRecognizer(panGesture)
}
@objc func handlePan(_ sender: UIPanGestureRecognizer) {
switch sender.state {
case .began:
// ジェスチャー位置をリセット
sender.setTranslation(.zero, in: interactiveView)
// ジェスチャーによるインタラクティブなアニメーション開始をシステムに通知
wantsInteractiveStart = true
// ジェスチャー開始時に実行したいトランジションを呼び出す(直接実行されずシステムが保持)
// 対応するアニメーションが設定されていれば UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning に処理が移る
// animated は必ず true でなければアニメーションされない
// Dismiss:
self.presented.dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil)
// Present:
//self.present(presenting,animated: true)
// Push:
//self.navigationController.push(presenting)
// Pop:
//self.navigationController.pop(animated: true)
case .changed:
// ジェスチャーの移動距離からアニメーションの進行度(0〜1)を計算
// 実際の計算はアニメーションの種類によって異なる
let translation = sender.translation(in: interactiveView)
guard translation.y >= 0 else {
sender.setTranslation(.zero, in: interactiveView)
return
}
let percentage = abs(translation.y / interactiveView.bounds.height)
// UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning のアニメーション進行度を更新
update(percentage)
case .ended:
// ジェスチャー終了時に進行度が閾値を超えているか判定
wantsInteractiveStart = false
if percentComplete >= thredhold {
// 超えていればアニメーション完了を通知
finish()
} else {
// 超えていなければアニメーションをキャンセルして元に戻す
cancel()
}
case .cancelled, .failed:
// キャンセルまたは失敗時
wantsInteractiveStart = false
cancel()
default:
wantsInteractiveStart = false
return
}
}
}
// UIViewController内にUIScrollView系コンポーネント(UITableView/UICollectionView/WKWebViewなど)がある場合のジェスチャー競合防止
// UIScrollViewがトップまでスクロールされている場合のみインタラクティブトランジションのジェスチャーを有効化
extension PullToDismissInteractive: UIGestureRecognizerDelegate {
func gestureRecognizer(_ gestureRecognizer: UIGestureRecognizer, shouldRecognizeSimultaneouslyWith otherGestureRecognizer: UIGestureRecognizer) -> Bool {
if let scrollView = otherGestureRecognizer.view as? UIScrollView {
if scrollView.contentOffset.y <= 0 {
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
return true
}
}
*sender.setTranslation( .zero, in:interactiveView) の理由についての補足ポイントはこちら<
私たちは、異なるジェスチャー操作の効果に応じて、異なるクラスを実装する必要があります。同じ連続した操作(Present + Dismiss)の場合は、一つにまとめることも可能です。
⚠️⚠️⚠️⚠️⚠️
wantsInteractiveStartは必ず適切な状態にしてください。インタラクティブなアニメーション中にwantsInteractiveStart = falseを設定すると画面が固まる原因になります;
アプリを再起動しないと正常に戻りません。
⚠️⚠️⚠️⚠️⚠️
interactiveView は必ず isUserInteractionEnabled = true にしてくださいね
もう少し設定を追加して確実にしましょう!
組み合わせ
ここで Delegate を設定し、Class を作成すれば、目的の機能が実現できます。
それでは、早速完成したサンプルを紹介します。
自作の下に引っ張って閉じるページ効果
自作の下方向スワイプの利点は、市販のすべての iOS バージョンをサポートでき、オーバーレイの割合や閉じるトリガー位置を制御でき、アニメーション効果をカスタマイズできることです。
右上の + ボタンをタップしてページを表示する
これは HomeViewController が HomeAddViewController を Present し、HomeAddViewController が Dismiss する例です。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
import UIKit
class HomeViewController: UIViewController {
@IBAction func addButtonTapped(_ sender: Any) {
guard let homeAddViewController = UIStoryboard(name: "Main", bundle: nil).instantiateViewController(identifier: "HomeAddViewController") as? HomeAddViewController else {
return
}
// transitioningDelegate は対象のViewControllerまたは現在のViewControllerで処理可能
homeAddViewController.transitioningDelegate = homeAddViewController
homeAddViewController.modalPresentationStyle = .custom
self.present(homeAddViewController, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
}
import UIKit
class HomeAddViewController: UIViewController {
private var pullToDismissInteractive:PullToDismissInteractive!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// 画面遷移のインタラクション情報をバインド
self.pullToDismissInteractive = PullToDismissInteractive(self, self.view)
}
}
extension HomeAddViewController: UIViewControllerTransitioningDelegate {
func interactionControllerForDismissal(using animator: UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning) -> UIViewControllerInteractiveTransitioning? {
return pullToDismissInteractive
}
func animationController(forPresented presented: UIViewController, presenting: UIViewController, source: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
return PresentAndDismissTransition(false)
}
func animationController(forDismissed dismissed: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
return PresentAndDismissTransition(true)
}
func interactionControllerForPresentation(using animator: UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning) -> UIViewControllerInteractiveTransitioning? {
// ここではPresentの操作ジェスチャーなし
return nil
}
}
import UIKit
class PullToDismissInteractive: UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition {
private var interactiveView: UIView!
private var presented: UIViewController!
private var completion:(() -> Void)?
private let thredhold: CGFloat = 0.4
convenience init(_ presented: UIViewController, _ interactiveView: UIView,_ completion:(() -> Void)? = nil) {
self.init()
self.interactiveView = interactiveView
self.completion = completion
self.presented = presented
setupPanGesture()
wantsInteractiveStart = false
}
private func setupPanGesture() {
let panGesture = UIPanGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: #selector(handlePan(_:)))
panGesture.maximumNumberOfTouches = 1
panGesture.delegate = self
interactiveView.addGestureRecognizer(panGesture)
}
@objc func handlePan(_ sender: UIPanGestureRecognizer) {
switch sender.state {
case .began:
sender.setTranslation(.zero, in: interactiveView)
wantsInteractiveStart = true
self.presented.dismiss(animated: true, completion: self.completion)
case .changed:
let translation = sender.translation(in: interactiveView)
guard translation.y >= 0 else {
sender.setTranslation(.zero, in: interactiveView)
return
}
let percentage = abs(translation.y / interactiveView.bounds.height)
update(percentage)
case .ended:
if percentComplete >= thredhold {
finish()
} else {
wantsInteractiveStart = false
cancel()
}
case .cancelled, .failed:
wantsInteractiveStart = false
cancel()
default:
wantsInteractiveStart = false
return
}
}
}
extension PullToDismissInteractive: UIGestureRecognizerDelegate {
func gestureRecognizer(_ gestureRecognizer: UIGestureRecognizer, shouldRecognizeSimultaneouslyWith otherGestureRecognizer: UIGestureRecognizer) -> Bool {
if let scrollView = otherGestureRecognizer.view as? UIScrollView {
if scrollView.contentOffset.y <= 0 {
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
return true
}
}
以上で図のような効果が得られます。ここではチュートリアルのためにあまり複雑にせず、コードは見栄えが悪いですが、まだ多くの最適化や統合の余地があります。
特筆すべきことは…
iOS ≥ 13、View の内容に UITextView が含まれている場合、下に引き下げて閉じるアニメーション中に UITextView の文字が真っ白になり、一瞬ちらつく現象があります。(動画例) …
ここでの解決策は、アニメーション時に
snapshotView(afterScreenUpdates:)を使って元のビューのレイヤーの代わりにスクリーンショットを取得することです。
全画面右スワイプで戻る
全画面で右スワイプ戻るジェスチャーの解決策を探していると、Tricky な方法を見つけました: 画面に直接 UIPanGestureRecognizer を追加し、target と action をネイティブの interactivePopGestureRecognizer の action:handleNavigationTransition に指定します。 *詳しい方法はこちら<
その通りです!まさに Private API のように見え、審査で拒否されそうです。また、Swift で使えるかは不明で、Objective-C の Runtime 特有の機能を使っていると思われます。
正規の方法で行きましょう:
本記事の方法と同様に、navigationController の POP 戻り時に自分で処理を行い、全画面の右スワイプジェスチャーを追加してカスタムの右スワイプアニメーションと連携させるだけです!
その他は省略し、重要なアニメーションとインタラクション処理のクラスのみを掲載します:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
import UIKit
class SwipeBackInteractive: UIPercentDrivenInteractiveTransition {
private var interactiveView: UIView!
private var navigationController: UINavigationController!
private let thredhold: CGFloat = 0.4
convenience init(_ navigationController: UINavigationController, _ interactiveView: UIView) {
self.init()
self.interactiveView = interactiveView
self.navigationController = navigationController
setupPanGesture()
wantsInteractiveStart = false
}
private func setupPanGesture() {
let panGesture = UIPanGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: #selector(handlePan(_:)))
panGesture.maximumNumberOfTouches = 1
interactiveView.addGestureRecognizer(panGesture)
}
@objc func handlePan(_ sender: UIPanGestureRecognizer) {
switch sender.state {
case .began:
sender.setTranslation(.zero, in: interactiveView) // ジェスチャーの開始時に座標をリセット
wantsInteractiveStart = true
self.navigationController.popViewController(animated: true) // ナビゲーションコントローラでポップアニメーションを開始
case .changed:
let translation = sender.translation(in: interactiveView)
guard translation.x >= 0 else {
sender.setTranslation(.zero, in: interactiveView) // 左方向のスワイプを無効化
return
}
let percentage = abs(translation.x / interactiveView.bounds.width) // スワイプの進行度を計算
update(percentage) // 進行度に応じて遷移を更新
case .ended:
if percentComplete >= thredhold {
finish() // スワイプが閾値を超えたら遷移を完了
} else {
wantsInteractiveStart = false
cancel() // 閾値未満なら遷移をキャンセル
}
case .cancelled, .failed:
wantsInteractiveStart = false
cancel() // ジェスチャーがキャンセルまたは失敗した場合は遷移をキャンセル
default:
wantsInteractiveStart = false
return
}
}
}
上にスワイプしてフェードインする UIViewController
View上での上方向スワイプでフェードイン+下方向スワイプで閉じる、これはまさにSpotifyのプレーヤーのトランジション効果のようなものです!
この部分はやや複雑ですが、原理は同じなのでここでは掲載しません。興味のある方はGitHubのサンプル内容を参照してください。
注意すべき点は、上方向へのフェードイン時に、アニメーションは「.curveLinear 線形」を必ず使用することです。そうしないと、上方向のスワイプが指の動きに追従せず、スワイプ量と表示位置が比例しない問題が発生します。
完了!
完成図
この記事は非常に長く、整理と作成に多くの時間をかけました。ご辛抱強くお読みいただき、ありがとうございます。
全篇 GitHub サンプルダウンロード:
参考資料:
UIPresentationControllerを使ってシンプルで美しい下部ポップアップコンポーネントを作る(単純にPresentのアニメーション効果だけならこれで十分)
優雅なコードのラッピングを参考にする場合:
ご質問やご意見がございましたら、こちらからご連絡ください 。
Post は Medium から ZMediumToMarkdown によって変換されました。
本記事は Medium にて初公開されました(こちらからオリジナル版を確認)。ZMediumToMarkdown による自動変換・同期技術を使用しています。