iOS NSAttributedString:NSTextListとNSTextTabでリスト縮排を実現|SwiftでHTML風OL/UL/LI対応
iOS開発者向けにSwiftでNSAttributedStringのNSTextListとNSTextTabを使い、HTMLリストのOL/UL/LIのような縮排を簡単実装。面倒な手動調整不要で見やすいリスト表示が可能に。
本記事は AI による翻訳をもとに作成されています。表現が不自然な箇所がありましたら、ぜひコメントでお知らせください。
記事一覧
[iOS] NSAttributedString で NSTextList または NSTextTab を使ったリストのインデント実装検証
iOS SwiftでNSAttributedStringのNSTextListまたはNSTextTabを使ってHTMLのリスト(OL/UL/LI)風のインデント機能を実装する
技術的背景
以前、私のオープンソースプロジェクト「ZMarkupParser」を開発していた際に、HTML文字列をNSAttributedStringオブジェクトに変換するライブラリとして、NSAttributedStringだけで異なるHTML要素を実現する方法を研究・実装する必要がありました。その時に初めて、NSAttributedString Attributesの.paragraphStyle: NSParagraphStyle内のtextLists: [NSTextList]とtabStops: [NSTextTab]という、非常にマイナーな属性に触れましたが、ネット上の情報はほとんどありませんでした。
最初にHTMLリストのインデント変換を実装する際、この2つの属性を使って実現できる例を見つけました。まずはHTMLリストのインデントされたネスト構造を見てみましょう:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
<ul>
<li>ZMarkupParserは、HTML文字列をカスタマイズ可能なスタイルとタグでNSAttributedStringに変換する純粋なSwiftライブラリです。</li>
<li>ZMarkupParserは、HTML文字列をカスタマイズ可能なスタイルとタグでNSAttributedStringに変換する純粋なSwiftライブラリです。</li>
<li>
ZMarkupParserは、HTML文字列をカスタマイズ可能なスタイルとタグでNSAttributedStringに変換する純粋なSwiftライブラリです。
<ol>
<li>ZMarkupParserは、HTML文字列をカスタマイズ可能なスタイルとタグでNSAttributedStringに変換する純粋なSwiftライブラリです。</li>
<li>ZMarkupParserは、HTML文字列をカスタマイズ可能なスタイルとタグでNSAttributedStringに変換する純粋なSwiftライブラリです。</li>
<li>ZMarkupParserは、HTML文字列をカスタマイズ可能なスタイルとタグでNSAttributedStringに変換する純粋なSwiftライブラリです。</li>
</ol>
</li>
</ul>
ブラウザでの表示結果:
上図のように、リストは多層のネスト構造をサポートしており、階層ごとにインデントする必要があります。
その当時は他の多くのHTMLタグ変換作業もあり、作業量が多かったため、NSTextListやNSTextTabを使ってリストのインデントを簡単に試してみただけで、深く理解していませんでした。しかし、結果は期待外れで、間隔が広すぎたり、揃わなかったり、複数行で崩れたり、ネスト構造が不明瞭だったり、間隔の調整ができなかったりしました。少し試して解決策が見つからず、諦めてとりあえず応急処置的にレイアウトしました:
上の図のように効果が非常に悪いのは、実際には空白と記号 - を使って手動でレイアウトしているためで、インデント効果は全くありません。唯一の利点は、間隔が空白文字で構成されており、大きさを自分で調整できることだけです。
この件はそのまま放置され、1年以上オープンソースとしても特に修正はされませんでした;しかし最近になって、Listの変換を改善してほしいというIssuesが続々と寄せられ、開発者から解決のPRも提供されました。そのPRでのNSParagraphStyleの使い方を参考にして、再び新たな発見がありました;NSTextListやNSTextTabをよく研究すれば、完璧なインデント付きリスト機能を実現できる可能性があります!
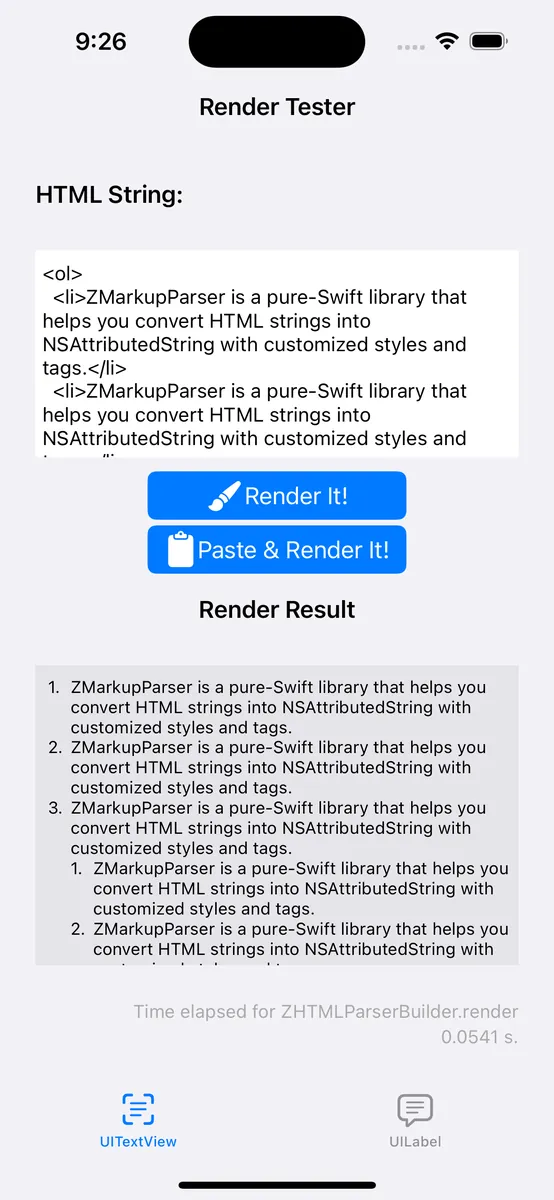
最終成果
いつものように、まず最終成果の画像を掲載します。
現在は ZMarkupParser ~>
v1.9.4以上のバージョンで、HTMLのリストアイテムを完璧にNSAttributedStringオブジェクトに変換できます。改行時のインデント維持
カスタムインデント間隔のサポート
ネスト構造のインデント対応
異なるリストアイテムスタイルのサポート(例:Bullet、Disc、Decimal…さらにカスタムシンボルも対応可能)
以下本文開始。
NSTextList または NSTextTab を使ったリストのインデント方法の検証
「または」であり「かつ」ではありません。NSTextList と NSTextTab は一緒に使う関係ではなく、それぞれ単独でリストのインデント機能を実現できます。
方法(1) NSTextList を使ったリストのインデント実装方法の検討
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
let listLevel1ParagraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle()
listLevel1ParagraphStyle.textLists = [textListLevel1]
let listLevel2ParagraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle()
listLevel2ParagraphStyle.textLists = [textListLevel1, textListLevel2]
let attributedString = NSMutableAttributedString()
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel1.marker(forItemNumber: 1))\tリストレベル1 - 1 文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel1ParagraphStyle]))
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel1.marker(forItemNumber: 2))\tリストレベル1 - 2\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel1ParagraphStyle]))
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel1.marker(forItemNumber: 3))\tリストレベル1 - 3\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel1ParagraphStyle]))
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel2.marker(forItemNumber: 1))\tリストレベル2 - 1\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel2ParagraphStyle]))
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel2.marker(forItemNumber: 2))\tリストレベル2 - 2 文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列文字列\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel2ParagraphStyle]))
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel1.marker(forItemNumber: 4))\tリストレベル1 - 4\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel1ParagraphStyle]))
textView.attributedText = attributedString
表示結果:
NSTextList が提供する Public API は非常に少なく、制御できるパラメータは以下の通りです:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// 項目の表示スタイル
var markerFormat: NSTextList.MarkerFormat { get }
// 順序付き項目の開始番号
var startingItemNumber: Int
// 順序付き番号項目かどうか (iOS 16以降で利用可能、このAPIは更新されている)
@available(iOS 16.0, *)
open var isOrdered: Bool { get }
// 項目番号を渡して項目記号の文字列を返す。順序付き番号項目でない場合は省略可能
open func marker(forItemNumber itemNumber: Int) -> String
NSTextList.MarkerFormat スタイル対応表:
- 識別度を高めるために、リストの位置を8に設定して表示します。
使用方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// NSMutableParagraphStyle を定義する
let listLevel1ParagraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle()
// リストアイテムのスタイルを定義し、項目の開始位置を設定する
let textListLevel1 = NSTextList(markerFormat: .decimal, startingItemNumber: 1)
// NSTextList を textLists 配列に割り当てる
listLevel1ParagraphStyle.textLists = [textListLevel1]
//
NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel1.marker(forItemNumber: 1))\項目一\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel1ParagraphStyle])
// ネストした子項目を追加する:
// 子項目リストアイテムのスタイルを定義し、項目の開始位置を設定する
let textListLevel2 = NSTextList(markerFormat: .circle, startingItemNumber: 1)
// 子項目用の NSMutableParagraphStyle を定義する
let listLevel2ParagraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle()
// 親と子の NSTextList を textLists 配列に割り当てる
listLevel1ParagraphStyle.textLists = [textListLevel1, textListLevel2]
NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel1.marker(forItemNumber: 1))\項目一之一\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel2ParagraphStyle])
// ネストした子項目のさらに子項目...
NSTextList を textLists 配列に追加し続けるだけでよい
\nを使って各リスト項目を区切る\t項目符号\tを使う目的は、attributedString.stringで純粋なテキスト文字列を取得したときにもリストの結果が得られるようにするためです。\t項目符号\tは表示されないため、項目符号の後に何を加工しても表示されません(例:.を追加しても表示に影響しません)。
使用上の問題点:
項目記号の左右の間隔を制御できない
項目記号をカスタマイズできず、数字の項目に「.
」を付けられない ->1.`親項目リストが非順序リスト(例:
.circle)で、子項目が順序付き数字リスト(例:.decimal)の場合、子項目のstartingItemNumberの設定が無効になることがあります。
NSTextList ができること、できる範囲は上記の通りですが、実際の製品開発ではあまり使いやすくありません。間隔が広すぎることや、数字項目に . がないため実用性が大幅に低下しています。ネット上で見つかったのは TextKit NSTextStorage を使って間隔を変更する方法 だけですが、私はこの方法はハードコーディングすぎると感じ、諦めました。唯一の利点は、Append textLists 配列を使って簡単にネストされたインデントの子リストを追加でき、複雑なレイアウト計算が不要なことです。
方法(2) NSTextTab を使ったリストのインデント実装方法の検討
NSTextTab は \t タブの占有位置を設定でき、デフォルトの間隔は 28 です。
私たちは NSMutableParagraphStyle の tabStops + headIndent + defaultTabInterval を設定することで、リストのような効果を実現しています。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
let textListLevel1 = NSTextList(markerFormat: .decimal, startingItemNumber: 1)
let textListLevel2 = NSTextList(markerFormat: .circle, startingItemNumber: 1)
let listLevel1ParagraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle()
listLevel1ParagraphStyle.defaultTabInterval = 28
listLevel1ParagraphStyle.headIndent = 29
listLevel1ParagraphStyle.tabStops = [
NSTextTab(textAlignment: .left, location: 8), // 図(1)のLocationに対応する設定
NSTextTab(textAlignment: .left, location: 29), // 図(2)のLocationに対応する設定
]
let listLevel2ParagraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle()
listLevel2ParagraphStyle.defaultTabInterval = 28
listLevel2ParagraphStyle.headIndent = 44
listLevel2ParagraphStyle.tabStops = [
NSTextTab(textAlignment: .left, location: 29), // 図(3)のLocationに対応する設定
NSTextTab(textAlignment: .left, location: 44), // 図(4)のLocationに対応する設定
]
let attributedString = NSMutableAttributedString()
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel1.marker(forItemNumber: 1)).\tList Level 1 - 1 StringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringString\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel1ParagraphStyle]))
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel1.marker(forItemNumber: 2)).\tList Level 1 - 2\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel1ParagraphStyle]))
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel1.marker(forItemNumber: 3)).\tList Level 1 - 3\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel1ParagraphStyle]))
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel2.marker(forItemNumber: 1))\tList Level 2 - 1\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel2ParagraphStyle]))
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel2.marker(forItemNumber: 2))\tList Level 2 - 2 StringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringString\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel2ParagraphStyle]))
attributedString.append(NSAttributedString(string: "\t\(textListLevel1.marker(forItemNumber: 4)).\tList Level 1 - 4\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: listLevel1ParagraphStyle]))
textView.attributedText = attributedString
tabStops配列はテキスト内の各\t記号に対応し、NSTextTabは配置方向(Alignment)と位置(Location)を設定できます(幅ではなくテキスト内の位置です!)headIndentは2行目以降の開始位置を設定し、通常は2つ目の\tの Location に設定します。これにより改行時に箇条書きの記号と揃います。defaultTabIntervalはデフォルトの\t間隔を設定します。テキスト内に他の\tがある場合も、この設定に従って間隔が調整されます。location:NSTextTab は方向と位置を指定するため、自分で位置を計算する必要があります。箇条書き記号の幅(桁数も影響します)+間隔+親項目のインデント距離を計算して、上図のような効果を出せます。箇条書きの記号は完全にカスタマイズ可能です。
もし
locationが誤っているか適合しない場合、直接改行が発生します。
上記の例は NSTextTab のレイアウト方法を理解してもらうために、計算の合計過程を簡略化して答えを直接書いています。実際の場面で使う場合は、以下の完全なコードを参考にしてください:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
let attributedStringFont = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: UIFont.systemFontSize)
let iterator = ListItemIterator(font: attributedStringFont)
//
let listItem = ListItem(type: .decimal, text: "", subItems: [
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 1 StringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringStringString", subItems: []),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 2", subItems: []),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 3", subItems: [
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 2 - 1", subItems: []),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 2 - 2 fafasffsafasfsafasas\tfasfasfasfasfasfasfasfsafsaf", subItems: [])
]),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 4", subItems: []),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 5", subItems: []),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 6", subItems: []),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 7", subItems: []),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 8", subItems: []),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 9", subItems: []),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 10", subItems: []),
ListItem(type: .circle, text: "List Level 1 - 11", subItems: [])
])
let listItemIndent = ListItemIterator.ListItemIndent(preIndent: 8, sufIndent: 8)
textView.attributedText = iterator.start(item: listItem, type: .decimal, indent: listItemIndent)
//
private extension UIFont {
func widthOf(string: String) -> CGFloat {
return (string as NSString).size(withAttributes: [.font: self]).width
}
}
private struct ListItemIterator {
let font: UIFont
struct ListItemIndent {
let preIndent: CGFloat
let sufIndent: CGFloat
}
func start(item: ListItem, type: NSTextList.MarkerFormat, indent: ListItemIndent) -> NSAttributedString {
let textList = NSTextList(markerFormat: type, startingItemNumber: 1)
return item.subItems.enumerated().reduce(NSMutableAttributedString()) { partialResult, listItem in
partialResult.append(self.iterator(parentTextList: textList, parentIndent: indent.preIndent, sufIndent: indent.sufIndent, item: listItem.element, itemNumber: listItem.offset + 1))
return partialResult
}
}
private func iterator(parentTextList: NSTextList, parentIndent: CGFloat, sufIndent: CGFloat, item: ListItem, itemNumber:Int) -> NSAttributedString {
let paragraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle()
// 例: 1.
var itemSymbol = parentTextList.marker(forItemNumber: itemNumber)
switch parentTextList.markerFormat {
case .decimal, .uppercaseAlpha, .uppercaseLatin, .uppercaseRoman, .uppercaseHexadecimal, .lowercaseAlpha, .lowercaseLatin, .lowercaseRoman, .lowercaseHexadecimal:
itemSymbol += "."
default:
break
}
// "1." の幅
let itemSymbolIndent: CGFloat = ceil(font.widthOf(string: itemSymbol))
let tabStops: [NSTextTab] = [
.init(textAlignment: .left, location: parentIndent),
.init(textAlignment: .left, location: parentIndent + itemSymbolIndent + sufIndent)
]
let thisIndent = parentIndent + itemSymbolIndent + sufIndent
paragraphStyle.headIndent = thisIndent
paragraphStyle.tabStops = tabStops
paragraphStyle.defaultTabInterval = 28
let thisTextList = NSTextList(markerFormat: item.type, startingItemNumber: 1)
//
return item.subItems.enumerated().reduce(NSMutableAttributedString(string: "\t\(itemSymbol)\t\(item.text)\n", attributes: [.paragraphStyle: paragraphStyle, .font: font])) { partialResult, listItem in
partialResult.append(self.iterator(parentTextList: thisTextList, parentIndent: thisIndent, sufIndent: sufIndent, item: listItem.element, itemNumber: listItem.offset + 1))
return partialResult
}
}
}
private struct ListItem {
var type: NSTextList.MarkerFormat
var text: String
var subItems: [ListItem]
}
簡単な
ListItemオブジェクトを宣言し、子リスト項目をカプセル化します。再帰的に組み合わせて、リスト項目の間隔と内容を計算します。NSTextListはmarkerメソッドのみでリスト記号を生成しますが、使用せずに自分で実装することも可能です。項目記号の前後の幅を広げるには、
preIndentとsufIndentを設定するだけで可能です。位置を計算する必要があるため、幅を計算する際に
Fontを使用します。そのため、正確な計算のために文字に.fontを設定する必要があります。
完成
最初は NSTextList を直接使えば実現できると期待していましたが、効果もカスタマイズ性も非常に低かったです。結局は NSTextTab を使って \t の位置を制御し、自分で項目記号を組み合わせる方法で対応しました。少し手間はかかりますが、効果は完璧に要件を満たせます!
目的は達成しましたが、依然として
NSTextTabの知識を完全には理解できていません(例えば、異なる方向?Location の相対位置?)。公式ドキュメントやネット上の情報が非常に少ないので、また機会があれば研究したいと思います。
この記事の完全サンプルダウンロード
広告
HTML文字列をNSAttributedStringに変換するツールで、カスタムスタイル指定やカスタムタグ機能に対応しています。
参考資料
- ObjC String Rendering / ObjC 中國 — 字符串渲染 この記事には NSAttributedString の完全な応用例があり、リストや表の機能実装も紹介されています。
ご質問やご意見がありましたら、こちらからご連絡ください 。
Post は ZMediumToMarkdown によって Medium から変換されました。
本記事は Medium にて初公開されました(こちらからオリジナル版を確認)。ZMediumToMarkdown による自動変換・同期技術を使用しています。